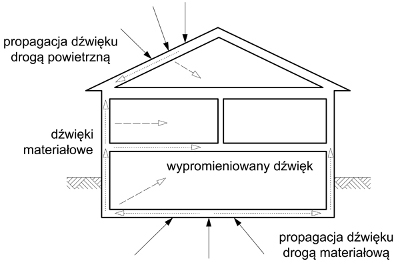
 Noise is sound waves of a certain frequency and power. Air noise can be distinguished (caused by contact with air) and contact noises (caused by contact with the material)
Noise is sound waves of a certain frequency and power. Air noise can be distinguished (caused by contact with air) and contact noises (caused by contact with the material)
We can eliminate or reduce excessive noise by eliminating or damping vibrations in the source itself and improving the acoustic insulation of partitions in the building, i.e. silencing the walls, ceilings, windows and doors.
The sound intensity is expressed in decibels [Db]. Fixed noise is that, for which the sound level changes over time by no more than by 5 Db. Unidentified noise is like that, for which the changes in the sound level are greater than 5 Db (Intermittent noise is also transient noise). The human ear perceives an increase in the sound level by 10 dB as a doubling of the sound intensity.
The permissible noise level depends on the purpose of the room and the time of day. The permissible sound level penetrating into the apartment from all noise sources located outside must not exceed:
during the day:
– 40 dB for living quarters
– 45 dB for kitchen and sanitary facilities,
at night time:
– 30 dB for living quarters
– 40 dB for kitchen and sanitary facilities.
The sound insulation index of a partition determines the number of decibels, which the partition can suppress. Minimum indicators of acoustic insulation [Db] for a multi-family residential building they are:
O 53 dB for ceilings,
O 52 dB for inter-apartment walls,
O 42 dB for walls between rooms in the same apartment.
Sound insulation is a mass derivative, which means, that insulation increases as the mass of the building material increases.
The parameter describing the sound insulation of wall materials is the weighted indicator of specific sound insulation Rw.
The strictest requirements apply to inter-apartment walls and walls separating apartments from corridors and staircases in multi-family buildings, where the permissible value of the indicator for the assessment of the approximate specific sound insulation R'A1 is 50 Db.